Understanding Break-Even Point (BEP) for Business Sustainability and Growth
In the fast-paced business world, a deep understanding of financial performance is key to sustainability and growth. One fundamental metric that plays a crucial role in financial analysis is the Break-Even Point (BEP). This article will thoroughly explore what BEP is, why calculating BEP is so crucial, and how this concept can be a strategic guide for your business in Indonesia, especially in this digital era.
What is BEP?
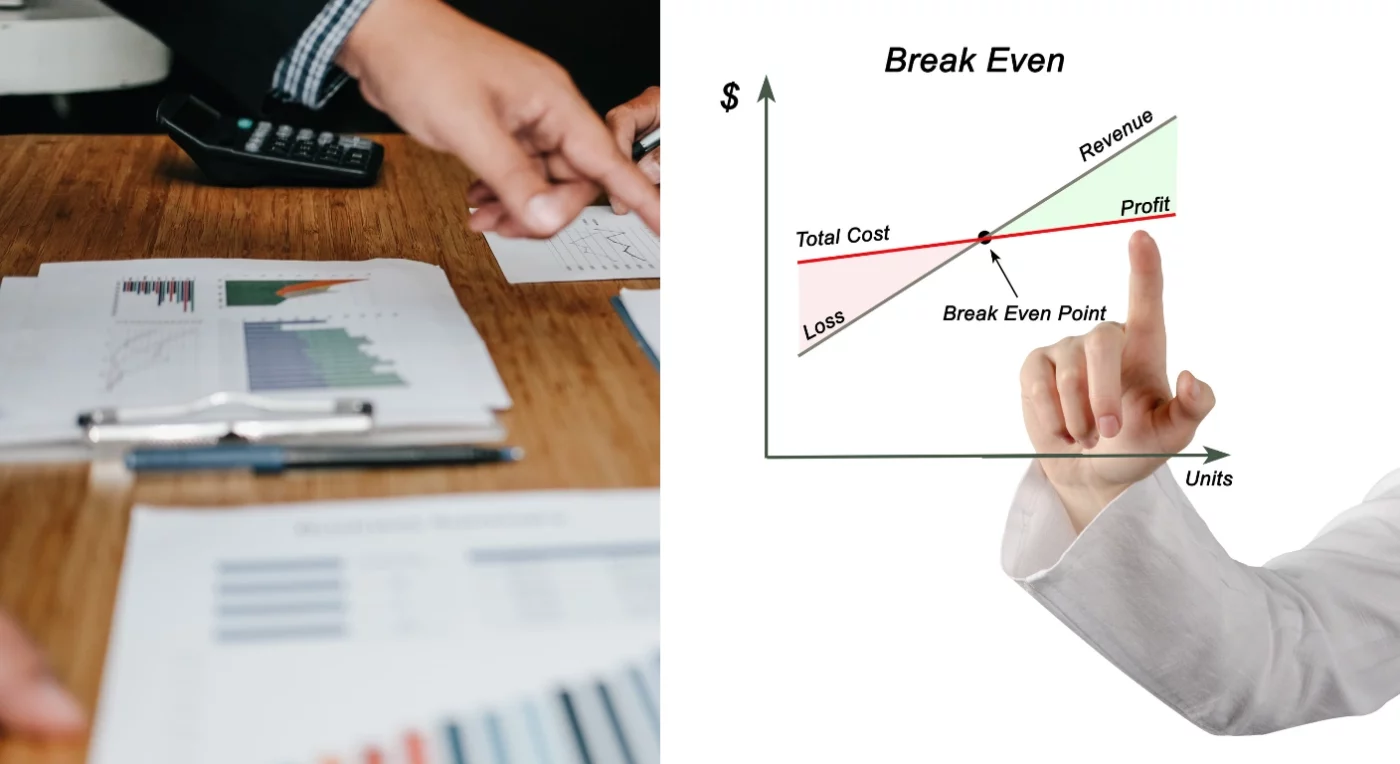
The Break-Even Point (BEP) is the condition where a company’s total revenue equals its total costs, resulting in neither profit nor loss. At the BEP, profit is zero, meaning the company is not making money or losing money. For the layperson, it’s often known as “returning on investment” or “breaking even.”
According to Syarifuddin Alwi (1990: 239), BEP is a state where a company experiences neither loss nor profit, thus achieving balance or breaking even. This BEP condition can arise if a company uses fixed costs in its operations, while its sales volume is just enough to cover both fixed and variable costs. In other words, BEP shows the amount of revenue a company needs to achieve to cover all existing costs. BEP is often referred to as an indicator of business operational success because it provides a clear picture of when a business will start generating profit.
The BEP concept centers on the idea of financial equilibrium, where financial investment meets financial return. For a company, this means that the revenue received from selling products or services precisely covers all costs, both fixed costs and variable costs. If sales fall below this point, the company will incur losses, while sales above this point will start generating profit. Fundamentally, BEP is the point where a company’s net profit is zero. It is the minimum threshold a company must reach to cover its operational costs.
The Purpose of Calculating BEP
The main purpose of calculating the Break-Even Point is to provide strategic information to company management for business decision-making. BEP has several specific objectives, including:
- Determining Optimal Production Capacity: BEP helps companies or business owners determine the remaining production capacity after reaching BEP and understand the projected maximum profit that can be obtained.
- Improving Operational Efficiency: BEP helps companies or business owners determine more efficient next business steps, such as replacing human resources with machines. This production automation can change fixed and variable costs and reduce production costs. At Mubarokah Digital, we understand the importance of operational efficiency. Our business automation services with n8n can help you identify areas where manual processes can be automated, thereby reducing variable costs and increasing efficiency.
- Analyzing Price Changes: BEP helps companies or business owners understand changes in profit value when product prices change.
- Anticipating Losses: BEP shows the break-even point, allowing companies or business owners to anticipate losses when sales decline.
- Knowing Total Production Costs: When calculating BEP, companies automatically also calculate the total costs incurred to produce a certain number of goods, including fixed costs and variable costs. This provides a clear picture of the company’s cost structure.
- Optimizing Financial Management: The primary goal of BEP is to optimize a company’s financial management. This includes efforts to reduce production and operational costs, and to keep these costs as minimal as possible without sacrificing product quality or quantity. By understanding BEP, companies can identify areas where cost efficiency can be improved.
Objectives and Benefits of BEP
BEP analysis has strategic objectives and benefits in corporate financial management.
BEP Objectives
These objectives include:
- Minimizing production and operational costs, and keeping these costs as low as possible without neglecting product quality and quantity.
- Maintaining the company’s product price level.
- Determining product prices with careful consideration, so that product prices are in line with planned profits and targets.
- Maximizing activity volume.
BEP Benefits
BEP provides various important benefits for business continuity:
- Determining the Right Selling Price: BEP simplifies the process of accurately determining the selling price of a product. It’s a metric used to help figure out the precise selling price. In digital marketing strategies, accurate pricing based on BEP can influence conversion and sales volume, which ultimately impacts your SEO performance and ad ROI.
- Anticipating Risk of Loss: BEP can provide a measurable risk analysis. From BEP calculations, business actors can anticipate inflated expenses that could impact business profit.
- Evaluating Business Performance: The BEP value can signal good or bad business performance for a certain period. If sales results are above BEP, the company makes a profit.
- Estimating Break-Even Time: With accurate Break-Even Point calculations, business actors can estimate the quantity of products to be sold and their sales period in the market.
- Analyzing Business Profitability: The value obtained from Break-Even Point calculations can serve as a basis for determining the amount of profit that can be reaped from the sales efforts of a business entity.
- As a Basis for Profit Calculation: In the business world, there is a term “profit margin,” which is a standard measure of profit for each product. If you want to determine the profit margin, the break-even point is the first thing to calculate.
- Estimated Return on Capital: Another benefit of the break-even point is to know the estimated return on capital.
- Determining Required Goods/Production Volume: BEP helps determine the volume of goods that must be produced and sold to reach the break-even point. Once this minimum production volume is known, entrepreneurs can project company profits and set realistic sales targets.
- Strategic Decision Making: BEP analysis allows companies to estimate how different price levels will affect the number of units that must be sold to cover costs. This helps in balancing competitive pricing with profitability requirements and revenue goals. Furthermore, by understanding BEP, companies can identify unnecessary or reducible expenses, enabling them to take more efficient steps to reduce cost burdens. BEP analysis also shows how changes in costs and strategies will affect profitability, allowing companies to assess risks and make data-driven investment or expansion decisions. It also helps estimate the type and amount of funding needed to achieve business goals.
- Funding Needs Estimation: Understanding the break-even point can help companies estimate what type of funding is needed for the business to operate smoothly, including the amount of funds needed to achieve business goals.
- Increased Profitability: BEP analysis indirectly increases business profitability by helping companies analyze profits and reduce the risk of loss. This allows companies to project profits from the company after determining production volume.
Difference Between COGS and BEP
Although both are important concepts in accounting and financial management, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) and Break-Even Point (BEP) have different definitions and functions.
Definition and Concept
- COGS (Cost of Goods Sold): COGS is how much it costs to produce a good or service. COGS represents all direct costs incurred to acquire the goods or services sold. COGS is calculated considering components such as beginning and ending inventory, and net purchases. COGS reflects the cost for each unit of product sold.
- BEP (Break-Even Point): BEP is used to project the sales volume needed to reach the break-even point between revenue and costs. BEP is the point where total revenue equals total costs incurred. BEP is not a cost, but rather an analytical point that shows the minimum sales volume required to cover all expenses.
Purpose of Use
- COGS: Used as a basis for determining the selling price of products to achieve desired profits. In addition, COGS calculation can be used as a reference to monitor the realization of production costs for management.
- BEP: Used to analyze the projection of how many units need to be produced or how much money needs to be received to reach the break-even point or return on capital. BEP is used for strategic planning, setting sales targets, risk evaluation, and making decisions related to price and production volume.
Relationship Between COGS and BEP
BEP price can be said to be the same as COGS, which is total cost divided by total production. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is the pure price of sales, the profit value in COGS is zero, and the COGS nominal is equal to BEP. COGS is a cost element that forms part of the BEP calculation, while BEP is an analytical result that shows when a company reaches its break-even point from its entire operations.
3 BEP Components: What are they?
Types of BEP
Break-Even Point can be divided into several types based on its calculation method:
- Break-Even Point Unit: This is the number of units a business needs to sell to cover its total costs and break even. It’s calculated by dividing total fixed costs by the contribution margin per unit. This calculation is very helpful for sales teams to understand the minimum sales volume that must be achieved before the company can sustainably pay all its expenses.
- Revenue Break-Even Point: This is the level of revenue a business needs to generate to cover its total costs and break even. Revenue Break-Even Point is calculated by dividing total fixed costs by the contribution margin ratio. This calculation focuses on the sales volume in monetary value required to achieve balance between revenue and costs.
- Time Break-Even Point: This is the amount of time it takes for a business to reach its Break-Even Point, based on fixed costs, selling price, and variable costs per unit. This is important for investors and business owners to understand how long it will take before their investment starts generating returns that cover initial and operational costs.
Basic BEP Components
Break-even point analysis only uses two main cost approaches:
- Fixed Cost: This refers to costs that do not change in total, even with changes in production or sales volume within certain limits. Examples include employee salaries, building rent, and machine depreciation. These costs must be incurred constantly, even if the company produces nothing.
- Variable Cost: This refers to costs that change in total according to changes in production or sales volume. Examples include electricity, internet, telephone, water, raw materials, and transportation costs. The more units produced, the higher the variable costs, and vice versa. It is important to accurately identify variable cost per unit as this is a key component in calculating the contribution margin.
- Price (Selling Price): This is the price determined after calculating fixed and variable costs, plus the company’s profit margin. The selling price per unit is the price set for each product or service sold by the company. This component is crucial as it directly affects total revenue and, in turn, the break-even point.
- Revenue: This refers to the income obtained from all sales made. In the context of BEP, total revenue at the break-even point equals total costs.
- Contribution Margin: The contribution margin is the difference between the selling price per unit and the variable cost per unit. It shows how much1 revenue from each unit sale is available to cover fixed costs and then contribute to profit. The higher the contribution margin per unit, the fewer units need to be sold to reach the break-even point. The contribution margin is an important analytical tool for managerial decision-making, planning pricing and production strategies, and evaluating product/service profitability.
BEP Formulas

There are several BEP formulas that can be used to calculate the Break-Even Point, depending on the type of analysis desired:
1. BEP per unit
BEP Unit Formula:BEP (in units)=Selling Price per Unit – Variable Cost per UnitFixed CostsOr it can be written as:BEP (in Units)=Contribution Margin per UnitFixed Costs
2. BEP Rupiah Formula
BEP Rupiah Formula:BEP (in Rupiah)=(Price per Unit – Variable Cost per Unit)Fixed Costs×Price per UnitOr it can be written as:BEP (in Rupiah)=Contribution Margin per UnitFixed Costs×Price per Unit
3. BEP Formula with Contribution Margin Ratio:BEP (Rupiah)
BEP Formula with Contribution Margin Ratio:BEP (Rupiah)=1−(Variable Cost per Unit / Selling Price per Unit)Fixed CostsOr:BEP (Rupiah)=Contribution Margin RatioFixed CostsContribution Margin Ratio: The ratio of contribution margin to total sales. This ratio is calculated as (Total Sales – Total Variable Costs) / Total Sales.
5. BEP Formula with Target Profit
BEP Formula with Target Profit:BEP with Target Profit (units)=(Selling Price per Unit – Variable Cost per Unit)(Fixed Costs + Target Profit)
BEP Examples
To provide a more concrete understanding, here are examples of BEP in units and in Rupiah.
Example 1: BEP Unit and Rupiah
A company produces shoes with the following data:
- Fixed Costs: Rp400,000,000
- Variable Cost per Unit: Rp2,000,000
- Selling Price per Unit: Rp3,000,000
BEP Unit Calculation:
BEP (in Units)=(3,000,000−2,000,000)400,000,000
BEP (in Units)=1,000,000400,000,000=400 units
BEP Rupiah Calculation:
BEP (in Rupiah)=(3,000,000−2,000,000)400,000,000×3,000,000
BEP (in Rupiah)=1,000,000400,000,000×3,000,000=Rp1,200,000,000
Interpretation: The company must produce and sell 400 units of shoes to reach the break-even point, which is the condition where total revenue equals total costs, with no profit or loss. Sales above 400 units will generate profit.
Example 2: Bicycle Company
A company that produces bicycles has the following data:
- Fixed Cost: Rp150,000,000
- Variable Cost per Unit: Rp1,000,000
- Selling Price per Unit: Rp2,500,000
Calculation:
BEP Unit=(2,500,000−1,000,000)150,000,000
BEP Unit=1,500,000150,000,000=100 units
Example 3: Electronics Company
PT Mandiri Sukses has the following data:
- Fixed Costs: Rp15,000,000
- Selling Price per Unit: Rp500,000
- Variable Cost per Unit: Rp250,000
BEP Unit Calculation:
BEP (units)=(500,000−250,000)15,000,000=60 units
BEP Rupiah Calculation:
BEP (Rupiah)=60 units×Rp500,000=Rp30,000,000
BEP in Rupiah
BEP in Rupiah is the break-even point calculated from the selling price in Rupiah currency. BEP Rupiah is similar to BEP price, but BEP Rupiah is more specific because its calculation must use Rupiah currency.
BEP Rupiah Formula
BEP Rupiah=(M/P)FC
Where:
- FC: Fixed Cost
- M: Margin (difference between selling price and variable price per unit)
- P: Price (selling price) per unit
Example of BEP Rupiah Calculation
Company X has the following data:
- Fixed Costs (FC): Rp100,000,000
- Variable Cost per Unit: Rp65,000
- Selling Price per Unit: Rp85,000
Calculation:
Margin = Selling Price – Variable Cost = 85,000 – 65,000 = 20,000
BEP Rupiah=(20,000/85,000)100,000,000=0.235100,000,000≈Rp425,531,915
Benefits of BEP in Rupiah
BEP in Rupiah helps understand the revenue figure that must be achieved to reach the break-even point. BEP in Rupiah is useful for knowing the minimum revenue target needed to reach the break-even point.
Implementing BEP in Digital Business
For business players in Indonesia operating in the digital realm, understanding BEP becomes even more relevant. In web development, mobile app development, and UI/UX design, initial costs (fixed costs) such as platform development or core team salaries can be very high. Meanwhile, variable costs such as server costs, digital advertising, or software licenses can fluctuate.
With careful BEP analysis, you can:
- Accurately determine the selling price of your digital products or services: Whether it’s the subscription price for a mobile application, web development costs, or UI/UX design packages, BEP will help you set prices that are not only competitive but also ensure profitability.
- Plan effective digital marketing strategies: By knowing the sales volume needed to reach the break-even point, you can allocate your digital marketing budget more efficiently. For example, how many leads must be generated from SEO campaigns or paid advertising to reach BEP? Mubarokah Digital can help you design SEO, SEM, and other digital campaign management strategies integrated with your BEP targets.
- Identify opportunities for business automation: Variable costs can be reduced through business process automation. For example, using n8n to automate marketing, sales, or customer service workflows can reduce manual labor costs and increase efficiency. This will directly affect your break-even point.
- Measure the performance of web development or mobile app development projects: By projecting BEP for each project, you can monitor progress and ensure that the project will generate profits as expected.
Conclusion
The Break-Even Point (BEP) is an extremely important financial analysis tool in modern business management. BEP not only helps companies determine their operational break-even point but also provides a strategic foundation for decision-making related to selling prices, production volume, and profit planning. A deep understanding of BEP, including its differences from COGS, the components involved, and various calculation methods, gives company management the ability to manage business risks more effectively.
In Indonesia’s competitive digital business landscape, the ability to analyze and utilize BEP is an invaluable asset. It empowers business owners and company leaders to make smarter decisions, reduce risk, and drive sustainable growth. By consistently applying BEP analysis, companies can optimize profitability and ensure long-term operational sustainability.
Are you ready to optimize your business strategy with in-depth BEP analysis and cutting-edge digital solutions? Mubarokah Digital is here to help. As a leading digital agency in Indonesia, we offer web development, mobile app development, UI/UX design, digital marketing, and business automation services that can be tailored to your company’s unique needs.
Don’t let uncertainty hinder your business growth. Contact us by clicking here to learn more about how we can help you reach your break-even point and exceed your profit targets!









Leave a Comment